Power Backup

Power Backup
 Ampace - 2025-08-04
Ampace - 2025-08-04
Portable Power Station vs Power Bank: Which Is Better?
Many people confuse backup power with portable power stations, thinking they work the same—both used during outages or on the go. But there are clear differences. A portable power station is more than just a bigger power bank; it’s a new way to meet your power needs.
When running high-power appliances like fridges, induction cookers, CPAP machines, or power tools, power banks usually can’t handle it. Portable power stations can. They have bigger capacity, more output ports (AC, DC, USB-C, car charger, etc.), and support outdoor use, emergencies, and backup power. Choosing Ampace gives you stable output, longer battery life, and smarter energy use.
This guide will break down the main differences between portable power stations and power banks, help you decide when to upgrade, and show why more people now rely on portable power stations at home and outdoors.
What is a Portable Power Station?
A portable power station is a high-capacity, multi-functional power device designed to supply electricity to a wide range of appliances and electronics. Unlike traditional power banks, portable power stations can support high-wattage devices like refrigerators, CPAP machines, electric tools, or even induction cooktops. They typically feature:
Large battery capacity (often 200Wh to over 2000Wh)
Multiple output ports (AC outlets, DC ports, USB-C, USB-A, car chargers)
High power output (100W to several kilowatts)
Support for diverse scenarios, including outdoor camping, emergency backup, off-grid living, and UPS (uninterruptible power supply) functionality
Advanced features like solar charging compatibility, smart power management, and long-lasting battery lifespans
Brands like Ampace offer reliable portable power stations with robust output, extended durability, and intelligent energy management, making them ideal for both home and outdoor use.
What is a Power Bank?
A power bank is a compact, portable device designed to charge low-power electronics like smartphones, tablets, earbuds, or smartwatches. Power banks are convenient for daily use but have limitations:
Smaller battery capacity (typically 5,000mAh to 30,000mAh, or roughly 18Wh to 110Wh)
Limited output ports (mostly USB-A, USB-C, sometimes wireless charging)
Low power output (usually 10W to 65W, insufficient for high-wattage appliances)
Primary use case: On-the-go charging for small devices
Lightweight and pocket-friendly, prioritizing portability over versatility
While power banks are great for keeping your phone alive during a busy day, they fall short when powering larger devices or supporting complex power needs.
Key Specifications to Consider When Buying
Whether you’re shopping for a power bank or a portable power station, understanding technical specifications is crucial to ensure the device meets your needs. Here are the most important factors to evaluate:
Battery Capacity
Power Bank: Measured in mAh (milliamp-hours). A 10,000mAh power bank can charge a typical smartphone 2–3 times.
Portable Power Station: Measured in Wh (watt-hours). A 500Wh station can power a 50W device for 10 hours.
Tip: Calculate your device’s power consumption (watts × hours) to estimate runtime.
Power Output (Wattage)
Ensure the device can handle the wattage of your appliances. For example, a fridge may require 100–200W, while a phone needs only 10–20W.
Look for surge power ratings on portable power stations, as some appliances draw extra power when starting.
Output Ports
Check for sufficient ports to charge multiple devices simultaneously.
For power stations, prioritize AC outlets for appliances and USB-C for modern gadgets.
Charging Methods
Power Banks: Typically charge via USB or wall adapters.
Portable Power Stations: Support wall charging, solar panels, or car chargers. Solar compatibility is ideal for off-grid use.
Safety Features
Look for protections against overcharging, overheating, short circuits, and low battery levels.
Power stations should include BMS (Battery Management Systems) for safe operation.
Portability
For power banks, prioritize lightweight designs for daily carry.
For power stations, consider weight and handles for transport, especially for camping or RV use.
Additional Features
Power Banks: Fast charging (PD/QC), wireless charging.
Power Stations: LCD displays, app-based monitoring, UPS mode, solar input.
Key Differences Between Portable Power Stations and Power Banks
Feature
Portable Power Station
Power Bank
Battery Capacity
200Wh–2000Wh+
18Wh–110Wh (5,000mAh–30,000mAh)
Power Output
100W–several kW, supports high-wattage appliances
10W–65W, limited to small devices
Output Ports
AC, DC, USB-C, USB-A, car charger, etc.
USB-A, USB-C, sometimes wireless
Use Cases
Camping, emergency backup, off-grid, UPS
Daily charging for phones, tablets, earbuds
Charging Options
Wall outlet, solar panels, car charger
Wall outlet, sometimes USB
Weight & Portability
Heavier (5–50 lbs), less pocket-friendly
Lightweight (0.2–1 lb), highly portable
Portable Power Stations Vs. Power Banks Which is better?
Choosing between a power bank and a portable power station comes down to your actual power needs. If you just need to charge your phone, earbuds, or tablet during daily use or short trips, a power bank is more convenient and affordable. But if you need to run high-power devices like a laptop, CPAP machine, mini fridge, or electric cooker—especially during camping, power outages, or off-grid situations—a portable power station is the better choice. Consider what you’ll be powering, for how long, and in what environment before making your decision.
Ampace Andes Portable Power Stations
Ampace portable power stations are ideal for charging phones during travel, camping, or power outages. They offer high-capacity, durable solutions with three models:
Ampace Andes 300
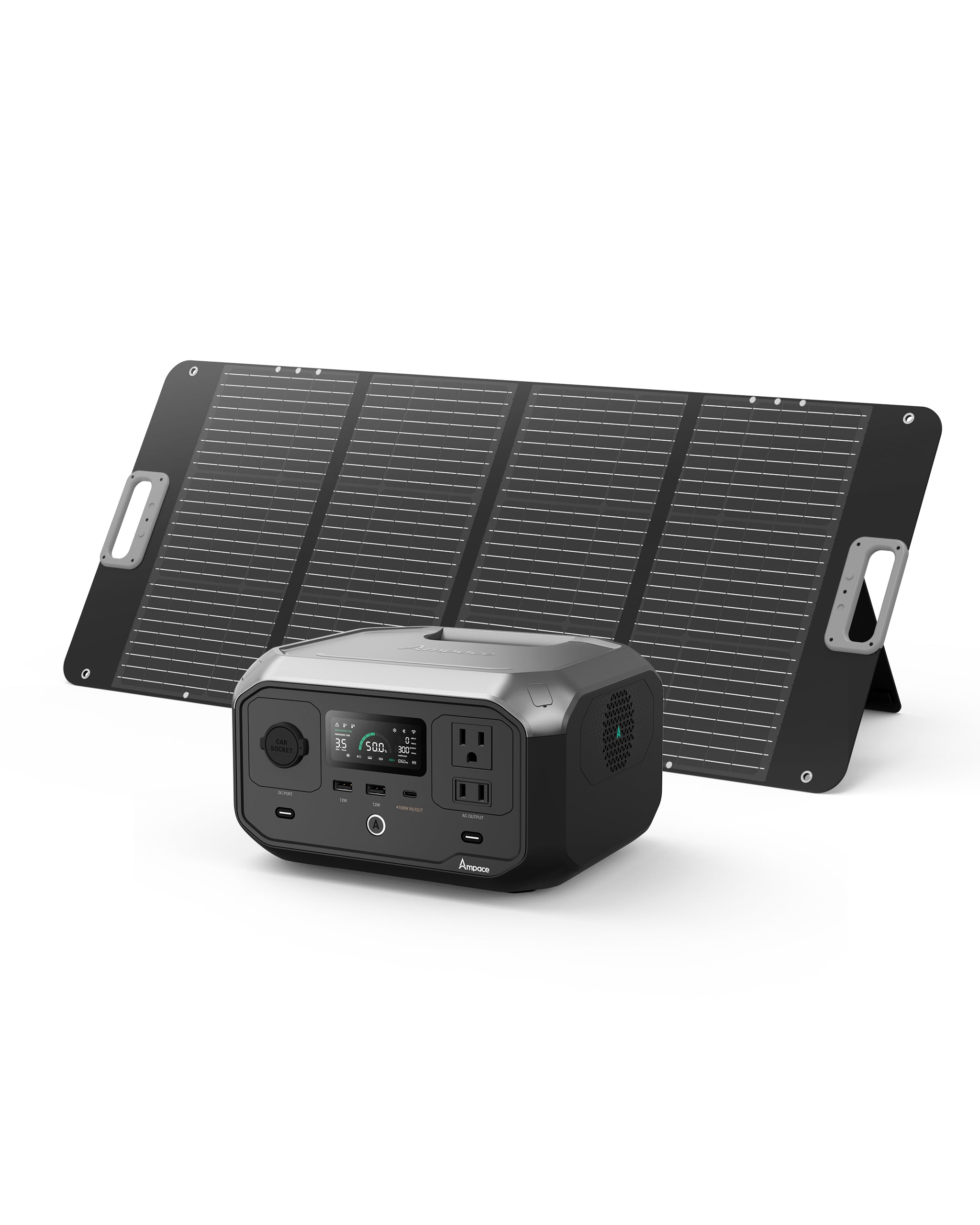
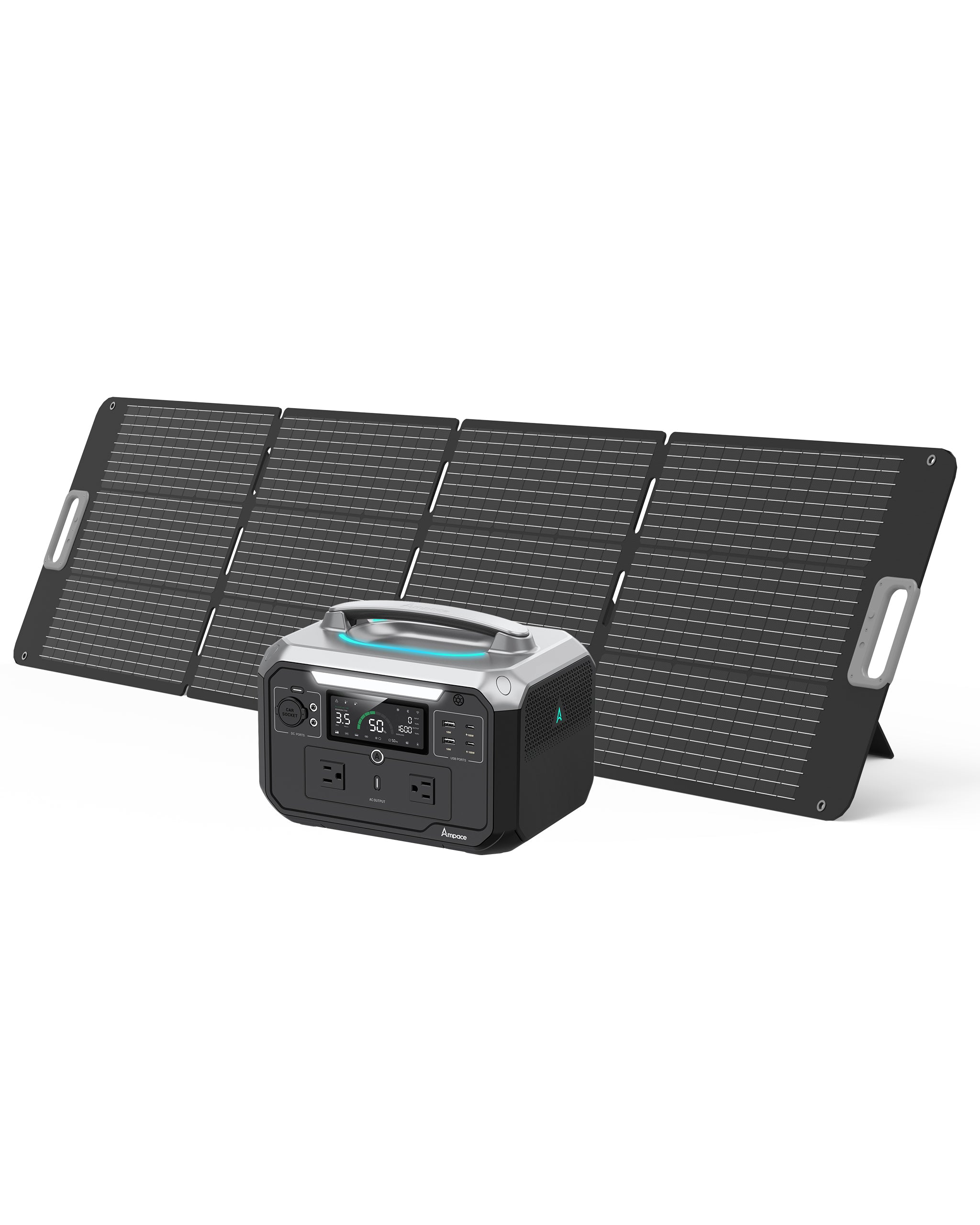
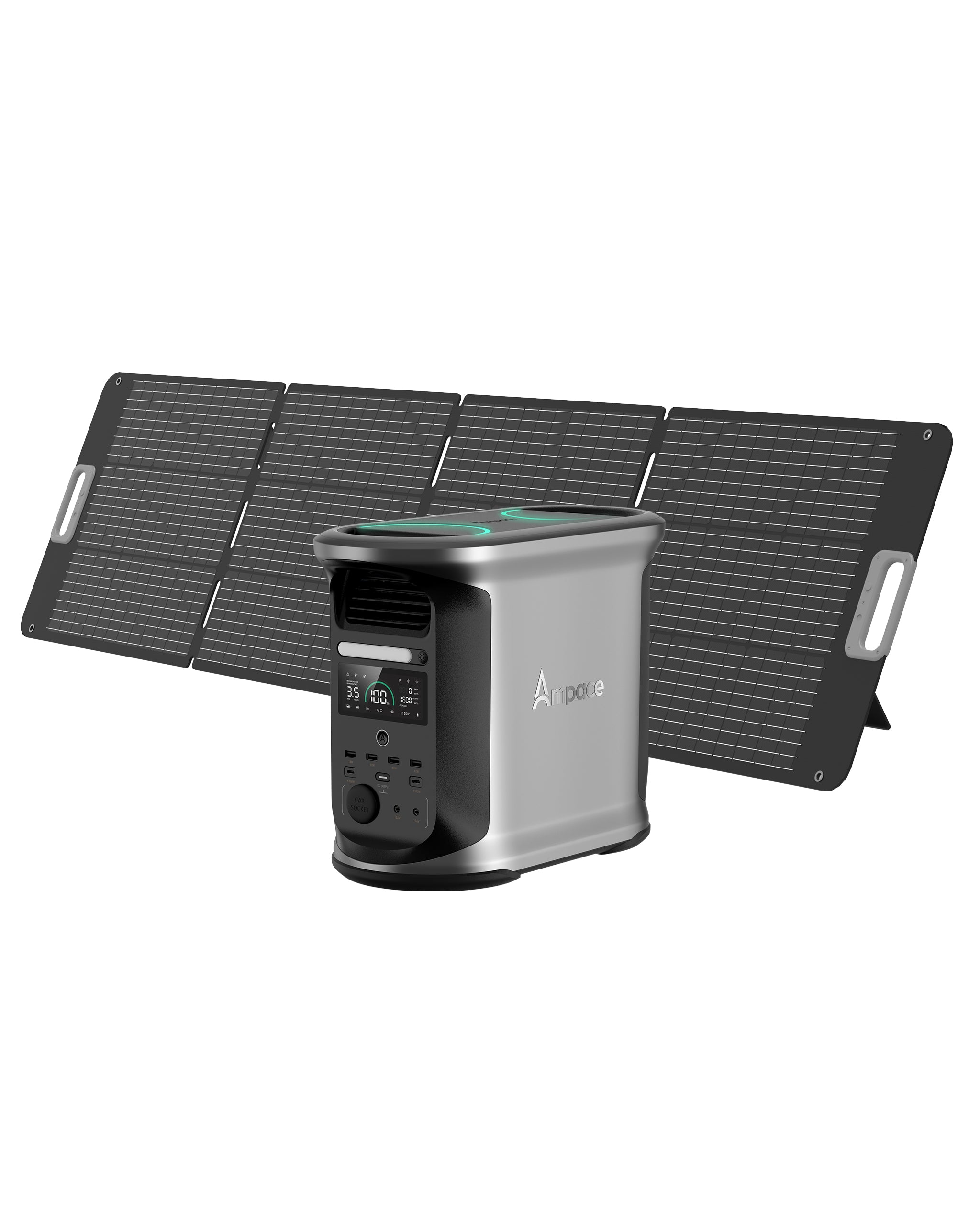
With a 266Wh capacity and 300W output (450W surge), this lightweight 8.2 lbs (3.72 kg) power station is perfect for camping or travel. It features six ports, including a 100W USB-C PD, two USB-A (12W), two AC outlets, and a 120W car socket. It charges to 80% in 45 minutes via AC, or in 2.5 hours with a 100W solar panel, and supports car charging. With 2500+ charge cycles (~10 years), it’s ideal for powering phones, tablets, or small appliances like mini-fridges during short outdoor trips.
Ampace Andes 600 Pro
Offering a 584Wh capacity and 600W output (1800W surge), this 16.8 lbs (7.6 kg)model is suited for RV camping or home backup. It includes nine ports: two AC outlets, two 100W USB-C, two 18W USB-A, a 120W car socket, and two 120W DC ports. It charges to 80% in 1 hour via AC or 3–5 hours with a 200W solar panel, with car charging supported. With 2000+ cycles (~10 years), it powers laptops, portable heaters, or CPAP machines with ease.
Ampace Andes 1500
Designed for heavy-duty needs, this 1462Wh power station delivers a robust 2400W output (3600W surge) and weighs 36.8 lbs (16.7 kg). It features 13 ports: four AC outlets, two 100W USB-C, four 18W USB-A, a 120W car socket, and two 120W DC ports. It fully charges in 55 minutes via AC or 3–5 hours with a 600W solar panel, with car charging available. With 6000+ cycles (~10+ years), it’s perfect for home outages or off-grid living, powering 99% of household appliances like fridges or electric pots.
 Ampace - 2025-08-04
Ampace - 2025-08-04
Power Backup
 Ampace - 2025-08-03
Ampace - 2025-08-03
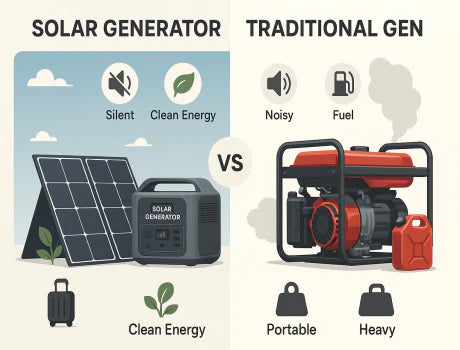
Solar Generators with Panels vs Traditional Generators - Which Wins?
The choice of the right power source can be tricky. Should you pick a solar generator with panels or a traditional fuel-powered one? Both have their strengths and weaknesses. Solar generators use sunlight to provide clean, quiet energy, perfect for camping, RVs, or eco-friendly backup. Traditional generators run on fuel, offering strong power but with noise and fumes. So, Solar Generators with Panels vs Traditional Generators - Which Wins? This blog will discuss how each works, compare their pros and cons, and help you find the best fit for your needs.
What Are Solar Generators with Panels?
Solar generators with panels are special devices that make electricity from sunlight. They comprise three main parts: a battery, an inverter, and solar panels.
The solar panels collect energy from the sun. This energy is then sent to the battery, which is stored for later use. The inverter changes the stored energy from the battery into the kind of electricity that most of our home devices use.
These generators are very useful for many things. People use them for camping, in RVs, and as backup power at home during outages. They are also good for people who want to use clean and eco-friendly energy. Solar generators are quiet, easy to use, and do not produce harmful smoke.
What Are Traditional Generators?
Traditional generators are machines that make electricity using fuel. The most common types use gasoline, diesel, or propane.
These generators have an internal combustion engine. When you add fuel, the engine burns it to create energy. This energy is then turned into electricity that you can use.
People often use traditional generators at construction sites, for emergency backup during power cuts, and in remote locations without regular electricity. They are strong and can provide much power, but they make noise and release smoke.
Head-to-Head Comparison
When choosing between a solar generator and a traditional gas generator, it is important to look at the details. Here's a simple comparison of the most important factors.
Portability & Ease of Use
Solar Generators: These are designed for easy use. Most are "plug-and-play" systems. You just set the panels in the sun and turn on the power station. They are often lighter than gas models. This makes them great for camping or taking on a trip. There is no heavy engine or fuel tank to carry.
Traditional Generators: They are usually heavier and bulkier. You have to carry and store a separate fuel can. Starting one often requires pulling a cord. Because of the fumes, you must be careful with where you put it.
Power Output & Capacity
Solar Generators: Their power is measured in watt-hours (Wh) for capacity and watts (W) for output. They can run many devices. Small units can charge phones and laptops. Larger models can power a refrigerator or a TV for a few hours. However, they may be unable to run high-power tools or multiple large appliances simultaneously.
Traditional Generators: These are known for high power. They can run heavy-duty tools and multiple appliances at the same time. If you have enough fuel, they can provide a continuous power supply. This makes them a strong choice for construction sites or large events.
Fuel & Running Costs
Solar Generators: The initial cost is often higher. But after you buy it, the running cost is zero. The "fuel" is sunlight, which is free. This saves you money in the long run.
Traditional Generators: The initial purchase price is usually lower. However, you have to buy fuel every time you use it. The price of gas or diesel can change. Over time, these costs add up and can become very expensive.
Noise Levels
Solar Generators: These are very quiet. They have no moving engine parts. You might hear a very light hum from the internal fan, but it's not much louder than a silent computer. This is perfect for camping, use in a residential area, or for indoor backup power.
Traditional Generators: They are very loud. The sound of the engine can be annoying and can disturb neighbours. Their noise can be as loud as a vacuum cleaner or a lawnmower, making them unsuitable for quiet places.
Maintenance Needs
Solar Generators: These are very low-maintenance. There are no engines, oil, or spark plugs. You need to keep the solar panels clean from dust or dirt. The batteries inside are built to last for many years.
Traditional Generators: They require a lot of regular maintenance. You must change the oil, replace the air filters and spark plugs, and ensure the fuel is fresh. If you do not use them for a while, the old fuel can cause problems.
Environmental Impact
Solar Generators: They are clean and green. They produce electricity by capturing sunlight, with zero emissions. They do not release any harmful fumes or greenhouse gases. This makes them an excellent choice for the environment.
Traditional Generators: They burn fossil fuels. This creates carbon emissions, which are bad for the environment and cause air pollution. They also cannot be used indoors because of the dangerous fumes.
Cost
Upfront Costs: The initial cost of buying a solar generator is generally higher than that of a traditional one. This is because of the cost of the solar panels and the battery technology.
Long-Term Costs: With a solar generator, your long-term costs are very low. You do not pay for fuel. You only need to clean the panels. Traditional generators, on the other hand, have high long-term costs. You must keep buying fuel and paying for regular maintenance like oil changes and filter replacements.
Return on Investment: A traditional generator is cheaper at first. But a solar generator often pays for itself over time. The money you save on fuel and maintenance can eventually compensate for the higher initial price.
Situational Recommendations
Traditional generators are often better for long-term home power backup. They can run a house for a long time if they have fuel. However, for a short outage, a solar generator can work well to power key devices.
Solar generators are the best choice for these activities. They are quiet, light, and do not require you to carry fuel. You can enjoy the outdoors without the noise or smell of a gas engine.
Both can work for emergencies. Traditional generators give you high power right away. Solar generators are good because they do not rely on a fuel supply that might not be available.
A solar generator is the winner. It is the only option that uses a renewable energy source. It has a zero-carbon footprint and is perfect for clean living off the grid.
Why Ampace Solar Generators Stand Out in Off-Grid Power
Clean, Renewable Energy Source
Ampace solar generators use energy from the sun. They do not burn fuel or release pollution. You can charge them with solar panels while camping, in your RV, or anywhere off-grid. With up to 600W solar input and high-efficiency panels, you get more power from every ray of sunshine.
Quiet and Easy to Use
These generators make almost no noise. You can use them at night or in quiet places without disturbance. They are simple to set up. Just unfold the solar panel, plug it in, and start charging. All cables and instructions are included in the box.
Low Maintenance Compared to Fuel Generators
Ampace solar generators do not have engines or moving parts like fuel generators. This means there is no oil to change, no fuel to store, and fewer parts to break. Just keep the panels clean and the generator will last for years.
No Fuel Costs – Save Money Over Time
You never have to buy gasoline, diesel, or propane. Once you have your Ampace solar generator and panels, the sun does the rest for free. This saves you much money in the long run and makes off-grid living more affordable.
Safe for Indoor and Outdoor Use
Ampace solar generators are safe to use anywhere. They do not produce smoke or fumes, so you can use them inside your tent, RV, or home. The panels are lightweight, waterproof, and dustproof. They are easy to carry and work in all kinds of weather.
Built to Last
Ampace generators use advanced EV-grade LFP batteries. They can last over 10 years, even with daily use. The Andes 1500 can be recharged up to 6,000 times, twice as long as other brands. Each model comes with a long warranty and friendly customer support.
Perfect for Any Adventure
Whether camping, travelling, or needing backup at home, Ampace solar generators are ready. With fast charging, high power output, and many outlet types, you can power all your devices with peace of mind.
Pros & Cons
Solar Generators
Pros: Clean and eco-friendly, quiet, low maintenance, free fuel (sunlight), safe for indoor use, very portable.
Cons: Higher upfront cost, lower power output, relies on sunlight, may not run all heavy appliances.
Traditional Generators
Pros: Lower upfront cost, high power output, runs heavy appliances, provides continuous power with fuel.
Cons: Loud and noisy, high long-term costs (fuel/maintenance), high maintenance needs, not eco-friendly, unsafe for indoor use, heavy and bulky.
Conclusion: Which One Wins?
Choosing between a solar generator and a traditional generator depends on your specific needs and priorities.
A traditional generator is a strong option if you need high, continuous power for heavy-duty tasks or long-term outages, and a lower initial cost is a priority.
A solar generator is the better choice if you value a quiet, clean, portable power source with low long-term costs and an eco-friendly footprint.
Ultimately, both are effective tools for providing power in different situations. What works best for one person might not be right for another. We hope this comparison helps you make the right choice for you! Feel free to leave any comments or questions below.
FAQs
Can I use both a solar and a traditional generator together?
Yes, you can. Many people use both to combine the benefits of quiet, clean solar power with a traditional generator's high-power output and reliability when needed.
How long do solar generator batteries last?
Most solar generator batteries, especially modern lithium-ion ones, last 5 to 15 years. The lifespan is measured in "cycles," Factors like usage habits and operating temperature can affect how long they last.
Are traditional generators safe to use indoors?
No, never. Traditional generators produce carbon monoxide, a deadly gas. They must be operated outdoors in a well-ventilated area, far from any windows, doors, or vents, to prevent the fumes from entering your home.
What about hybrid options?
Hybrid generators combine a fuel-powered engine with a battery system. They are more efficient, quieter, and environmentally friendly than traditional generators because the engine only runs when necessary to charge the battery or meet high power demands.
 Ampace - 2025-08-03
Ampace - 2025-08-03

Power Backup
 Ampace - 2025-07-28
Ampace - 2025-07-28
A Step-by-Step Guide to Preparing for a Long-Term Power Outage
Table of Contents
Understanding the Threat: Blackout vs. Brownout
The Four Pillars of Preparedness: Your Home Emergency Kit Checklist
The Power Plan: Your Modern Emergency Power Supply for Home
Choosing the Best Solar Generator for Home Backup
The Ampace Andes 1500: Your Family's Safety Net
Putting Your Plan into Action
It’s a feeling we all know. The lights flicker once, twice, then plunge you into an unnerving silence. In that sudden darkness, a wave of questions hits you. How long will this last? Is the food in the fridge going to spoil? How will I keep my phone charged? For most of us, a brief outage is just an inconvenience. But with grid instability, severe weather events, and the possibility of a rolling blackout becoming more common, it’s crucial to know how to prepare for a long-term power outage.
This isn’t about panic; it’s about peace of mind. It’s about knowing that you’ve taken the right steps to keep your family safe, comfortable, and connected, no matter what’s happening outside. This guide will walk you through everything you need to do, from building a foundational emergency kit to securing a modern, reliable power source that goes far beyond a simple flashlight.
Understanding the Threat: Blackout vs. Brownout
First, let’s quickly clear up some terms. What most of us call a blackout is a total loss of power. A brownout, on the other hand, is a temporary drop in voltage. While less severe, brownouts can still damage sensitive electronics. A solid preparedness plan should account for both, and even for more extreme, though less likely, scenarios. Some forward-thinking individuals even consider
EMP protection as part of their strategy, aiming for total resilience against any potential grid-down event.
The Four Pillars of Preparedness: Your Home Emergency Kit Checklist
A truly effective plan is built on four essential pillars. Think of this as your ultimate home emergency kit checklist, covering the absolute necessities to see you through an extended outage.
Pillar 1: Water
This is your most critical supply. The standard recommendation is to store at least one gallon of water per person, per day. For a family of four, a three-day supply means 12 gallons. For a longer-term outage, you’ll want significantly more. Don’t forget to have a method for water purification, like tablets or a filter, as a backup.
Pillar 2: Food
Stock up on non-perishable foods that your family will actually eat. Canned goods, dried fruit, peanut butter, and protein bars are excellent choices. Make sure you have a manual can opener. You’ll also need a way to cook without electricity, like a camp stove or a barbecue grill—just remember to use them outdoors in a well-ventilated area.
Pillar 3: Safety & First Aid
Your kit should include a comprehensive first-aid kit, any necessary prescription medications, flashlights or headlamps with extra batteries, and a whistle to signal for help. A battery-powered or hand-crank radio is essential for receiving emergency broadcasts when the internet and cell service are down.
Pillar 4: Power
This is where modern preparedness truly separates itself from the past. In today’s world, being without power means being cut off. It means losing hundreds of dollars in spoiled food, being unable to run critical medical devices, and losing your connection to the outside world. A modern plan requires a modern emergency power supply for home.
The Power Plan: Your Modern Emergency Power Supply for Home
When you think of backup power, you might picture a noisy, gas-guzzling generator that you can’t run indoors. Thankfully, technology has come a long way. Solar generators offer a clean, quiet, and safe alternative that’s perfect for keeping your home running.
During a long-term outage, a reliable power station isn’t a luxury—it’s a necessity. It’s the tool that lets you:
Save your food: Knowing how to keep fridge cold without power is simple when you can just plug it in. A good power station can run a standard refrigerator for hours, saving your groceries and your budget.
Stay healthy: For those who rely on medical devices like a CPAP machine, uninterrupted power is non-negotiable.
Prevent disaster: In a storm, powering a sump pump can be the one thing that saves your basement from flooding.
Remain connected: Keep phones, laptops, and your Wi-Fi router powered up to stay in touch with loved ones and receive critical updates.
Choosing the Best Solar Generator for Home Backup
So, what should you look for in the best solar generator for home backup? It comes down to a few key factors:
Capacity (Wh): Measured in watt-hours, this tells you how much energy the battery can store. For home backup, you’ll want a unit with significant capacity to run essential appliances.
Output (W): This is how much power the station can deliver at once. You need enough wattage to handle not just the running power of your appliances, but also the initial "surge" of power they need to start up.
Battery Type (LiFePO4): Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) is the gold standard for safety and longevity. These batteries can last for thousands of charge cycles, giving you a reliable power source for a decade or more.
UPS Functionality: An Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) is a game-changer. It means the power station can detect an outage and switch over to battery power in milliseconds, so your sensitive electronics and medical devices don’t even flicker.
Charging Options: The best units can be recharged quickly from a wall outlet before a storm hits, but also have solar charging capability to provide potentially endless power during a multi-day outage.
The Ampace Andes 1500: Your Family's Safety Net
When you look at all the critical features, one unit stands out: the Ampace Andes 1500. It’s not just a power station; it’s a complete home resilience strategy.
With a massive 1462Wh capacity and a powerful 2400W output (3600W surge), the Andes 1500 is engineered to handle 99% of household appliances. It uses an advanced, EV-grade.
LiFePO4 battery designed for over 6,000 cycles—that’s more than 10 years of daily use.
Here’s what to do during a power outage with the Andes 1500 on your side:
Keep Your Kitchen Running: Don’t worry about your food. As one user in north Texas shared after a recent storm, "The unit charges very quickly, and kept our fridge, chest freezer, fans, and TV running during the entire 2 day outage by using some solar panels to charge the unit".
Power Critical Medical Equipment: The Andes 1500 features a lightning-fast <20ms UPS switchover, ensuring that life sustaining equipment like CPAP machines never miss a beat.
Stay Safe and Comfortable: It operates at a whisper-quiet 30dB, so you can run it indoors without the noise or dangerous fumes of a gas generator.11 It’s powerful enough to run fans, lights, your router, and even a coffee maker to bring a little normalcy to a stressful situation.
Recharge with the Sun: When the outage stretches on, you’re not helpless. The Andes 1500 can be fully recharged with solar panels, giving you a sustainable source of off-grid power. And if you have a chance to prepare, it recharges from a wall outlet in an incredible55 minutes.
Putting Your Plan into Action
Feeling prepared is feeling empowered. You don’t have to be overwhelmed. Just follow these simple steps.
Build Your Kit: Go through the four pillars and gather your essential supplies of water, food, and safety equipment.
Secure Your Power: An outage is not the time to discover your power solution is inadequate. Investing in a reliable, powerful solar generator like the Ampace Andes 1500 is an investment in your family’s safety.
Practice Your Plan: Don’t wait for an emergency. Do a dry run. Unplug your fridge and see how to connect it to the power station. Make sure everyone in the family knows the plan.
Stay Informed: Have a battery-powered radio and know your local emergency alert channels.
A long-term power outage can be a daunting event, but it doesn’t have to be a catastrophe. With a solid plan and the right tools, you can face it with confidence, knowing you’ve done everything you can to keep your home and your loved ones secure.
 Ampace - 2025-07-28
Ampace - 2025-07-28

Power Backup
 Ampace - 2025-07-20
Ampace - 2025-07-20
How Many amps does a MicroWave Use
Table of Contents
What Are Microwave Amps?
Definitions of Amps, Volts, Watts, and Running Watts
Amperes and Wattage of Different Types of Microwaves
Ampace Solar Generators for Microwaves
Energy-Saving Tips for Microwaves
Conclusion
Microwaves are typically among the most power-hungry household appliances. Most home microwaves draw between 5 and 12.5 amps at 120 volts, with startup surge currents potentially reaching up to twice that amount. To support such high-powered devices, a power system capable of handling both high surge and continuous power is required—such as a dedicated circuit or a portable power station.
Household microwaves usually need 600 to 1500 watts of running power, while the surge power at startup can reach 1200 to 3000 watts. Therefore, the power system must have sufficient capacity and stability to prevent power interruptions or equipment damage. Additionally, using a dedicated 15- or 20-amp circuit can help avoid circuit overload, and for backup power, it's important to choose a device that supports high surge power—such as the Ampace portable power station.
What Are Microwave Amps?
Microwave amps refer to the electrical current (measured in amperes) that a microwave oven draws from a power source to operate its components, primarily the magnetron, which generates microwaves for cooking. The ampere (amp) is a unit of electrical current, indicating the "flow rate" of electricity through the appliance. Knowing a microwave's amp draw is essential to ensure it operates safely on your home's electrical circuit, especially when paired with other appliances, and to select appropriate backup power solutions.
Microwaves typically require significant power, especially during startup, due to the energy needed to initiate the magnetron and other components. Understanding this helps prevent circuit overloads, tripped breakers, or electrical hazards, particularly in homes with limited electrical capacity or when using alternative power sources like solar generators.
Definitions of Amps, Volts, Watts, and Running Watts
To fully grasp microwave power consumption, it’s important to understand the following electrical terms:
Amps (Amperes)
Amps measure the rate of electrical current flowing through an appliance. Think of it as the volume of electricity being used. For a microwave, the amp draw reflects how much current is needed to power the magnetron, fan, and control systems. The formula to calculate amps is:Amps (A) = Watts (W) ÷ Volts (V).For example, a 1000W microwave operating at 120V draws approximately 8.33 amps (1000 ÷ 120 = 8.33).
Volts
Volts measure the electrical potential difference, or the "pressure" that drives current through a circuit. In North America, standard household microwaves typically operate at 120 volts, while some commercial models may use 220–240 volts in other regions.
Watts: Watts measure the rate of power consumption or production, indicating how much energy an appliance uses per second. For microwaves, wattage reflects the total power needed to run the appliance. You can calculate watts using:Watts (W) = Volts (V) × Amps (A).
Running Watts
Running watts refer to the continuous power required to keep the microwave operating after startup. Microwaves often have a brief surge (inrush current) when the magnetron starts, which can be 1.5 to 2 times the running wattage. For example, a microwave rated at 1000 running watts may require up to 2000 watts momentarily during startup.
These terms are critical for calculating a microwave’s power needs, ensuring proper circuit allocation, and selecting a suitable backup power source.
Amperes and Wattage of Different Types of Microwaves
Microwave ovens vary in size, design, and features, which directly affect their power consumption. Below is a breakdown of typical amperage and wattage for different types of microwaves at 120 volts (standard U.S. household voltage):
Compact/Countertop Microwaves (600–800W):These smaller models, often used in dorms, offices, or small kitchens, consume 600–800 watts. At 120V, they draw approximately 5–6.7 amps during operation. Startup surges may require up to 10–13.4 amps. These microwaves are ideal for light use, such as reheating meals or making popcorn.
Standard Household Microwaves (900–1200W):Common in most homes, these microwaves use 900–1200 watts, drawing 7.5–10 amps during normal operation. Startup surges can reach 15–20 amps. They offer a balance of power and versatility for everyday cooking tasks.
High-Power/Convection Microwaves (1200–1500W):These advanced models, often with convection or grilling features, consume 1200–1500 watts, equating to 10–12.5 amps at 120V. Startup surges may demand 20–25 amps. They are suitable for larger households or those requiring additional cooking functions.
Commercial Microwaves (1800–2500W):Used in restaurants or cafeterias, these heavy-duty models consume 1800–2500 watts, drawing 15–20.8 amps during operation. Startup surges can exceed 30 amps, often requiring a dedicated 20-amp circuit or higher. These microwaves are designed for frequent, high-volume use.
Microwave Type
Wattage Range
Running Amps (at 120V)
Startup Surge Amps
Typical Use Case
Compact/Countertop Microwaves
600–800W
5–6.7A
10–13.4A
Light use: reheating meals, making popcorn (dorms, offices, small kitchens)
Standard Household Microwaves
900–1200W
7.5–10A
15–20A
Everyday cooking tasks (most homes)
High-Power/Convection Microwaves
1200–1500W
10–12.5A
20–25A
Larger households, advanced cooking (convection, grilling)
Commercial Microwaves
1800–2500W
15–20.8A
>30A
Frequent, high-volume use (restaurants, cafeterias)
To determine your microwave’s exact power consumption, check the label (usually located on the back or inside the door) for wattage or amperage ratings. Alternatively, use a power meter for precise measurements. Note that older microwaves may be less efficient, drawing more amps than newer, Energy Star-certified models.
Ampace Solar Generators for Microwaves
For those looking to power microwaves during outages, camping, or off-grid living, Ampace offers reliable and efficient portable power stations. These solar generators are designed to handle the high startup surges and continuous power demands of microwaves, making them an excellent choice for backup power. Below are two Ampace solutions tailored for microwave use:
Ampace Andes 1500
With a 1462Wh capacity and 2400W output (3600W surge), Ampace Andes 1500 portable power station can handle most household microwaves, including high-power models with startup surges up to 3600W. It’s ideal for powering microwaves during extended outages or off-grid scenarios, ensuring your appliance runs smoothly. Paired with Ampace portable solar panels, it can harness solar energy to provide a sustainable power supply.
Ampace Andes 600 Pro
Ampace Andes 600 Pro offering a 584Wh capacity and 600W output (1800W surge), this compact power station is suitable for smaller microwaves (600–800W) with lower startup demands. Its portability makes it perfect for camping, RV trips, or emergency backup for compact microwaves in small spaces.
Energy-Saving Tips for Microwaves
To reduce your microwave’s power consumption and optimize its use with solar generators or household circuits:
Choose Energy Star Models: These microwaves are designed to use less power, reducing amp draw by up to 20% compared to standard models.
Use Appropriate Settings: Lower power settings for tasks like defrosting can reduce energy use.
Minimize Runtime: Heat food in shorter intervals and avoid overcooking to save power.
Maintain Efficiency: Keep the microwave clean and ensure the door seals tightly to prevent energy loss.
Avoid Overloading Circuits: Plug your microwave into a dedicated 15- or 20-amp circuit to prevent tripping breakers, especially when using high-power models.
FAQ
How many amps does a microwave pull?
A typical household microwave draws between 5 and 12.5 amps at 120 volts during regular use. Startup surges may temporarily increase the draw to 10–25 amps, depending on the model.
What size breaker is needed for a microwave?
Most household microwaves require a dedicated 15-amp or 20-amp circuit breaker to avoid tripping and ensure safe operation, especially for units rated above 1000 watts or those with convection features.
How many amps does a refrigerator use?
A standard refrigerator typically draws 3 to 6 amps during normal operation at 120V. However, startup surges can push that to 15 amps or more momentarily.
Can a portable power station run a microwave?
Yes, but only if the power station can handle the microwave’s running watts and surge power. For example, a 1000W microwave may need up to 2000W surge capacity. Models like the Ampace Andes 1500 are suitable for this.
Is it safe to plug a microwave into a power strip?
No. Microwaves should not be plugged into standard power strips, as they draw high current that can overheat the strip and cause electrical hazards. Always use a dedicated wall outlet.
 Ampace - 2025-07-20
Ampace - 2025-07-20

Power Backup
 Ampace - 2025-07-10
Ampace - 2025-07-10
Emergency Power Buying Guide: What to Look For?
Table of Contents
What Is an Emergency Power Supply?
What Are the Benefits of an Emergency Power Supply?
Types of Emergency Power Supplies
Propane Generator vs. Solar Generator: Which to Choose?
Ampace Solar Generators for Emergencies
No one enjoys the darkness and helplessness that come with a power outage, which often strikes without warning. To prevent food spoilage in your fridge, keep your electronic devices connected, and ensure your lighting system remains functional, we recommend preparing a high-capacity emergency power supply. It offers your home a tangible sense of security. Ampace emergency power solutions keep you powered up and prepared.
What Is an Emergency Power Supply?
An emergency power supply is a backup power source that steps in when the grid fails, providing continuous electricity during outages. Advanced emergency power supplies even support solar charging, ensuring stable power during prolonged outages, making them ideal for homes, outdoor activities, commercial settings, and emergency situations.
Typically composed of generators, batteries, and other equipment, an emergency power supply kicks in when the primary power source fails, protecting lives and property. It functions as an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) or backup power source, ensuring critical devices remain operational.
What Are the Benefits of an Emergency Power Supply?
Investing in a high-performance emergency power supply isn’t just about handling unexpected outages—it also brings convenience to daily life and work:
Uninterrupted Daily Life: Even during a grid outage, your fridge, router, lights, and phone can continue running, keeping your routine intact.
Protecting Critical Equipment: For power-dependent medical devices (like ventilators or insulin pumps), an emergency power supply prevents damage due to power cuts.
Handling Extreme Weather and Disasters: During typhoons, heavy rain, earthquakes, or other emergencies, an emergency power supply becomes a vital survival tool, supporting lighting, communication, and basic needs.
Supporting Outdoor and Remote Work: Whether at a campsite, in a vehicle, or at a remote construction site, emergency power supplies provide reliable electricity for diverse needs.
Eco-Friendly Options: Many modern emergency power supplies support solar or rechargeable batteries, reducing reliance on traditional fuels and promoting a greener, low-carbon lifestyle.
Types of Emergency Power Supplies
When choosing an emergency power supply, understanding the features and use cases of different types is crucial. Below, we compare two common options: propane generators and solar generators.
Propane Generator
Propane generators run on liquid propane gas (LPG) and are a traditional, reliable choice for emergency power. They’ve been widely used for decades in both residential and commercial settings due to their consistent performance and high power output. Here are their key features:
Advantages:
High Power Output: Propane generators typically deliver high wattage, suitable for powering large appliances or an entire household.
Long Runtime: With sufficient propane fuel, they can run for hours or even days.
Reliable Performance: Unaffected by weather or light conditions, they’re ideal for various environments.
Easy Fuel Storage: Propane tanks are convenient to store, and the fuel has a long shelf life, perfect for long-term backup.
Disadvantages:
Noise and Emissions: Propane generators produce noise and exhaust fumes, making them unsuitable for indoor use and less environmentally friendly.
Fuel Dependency: They require regular fuel refills, which can add costs and safety concerns for storage and transport.
Higher Maintenance: Regular maintenance, such as oil changes and part cleaning, is needed for reliable operation.
Solar Generator
Solar generators convert sunlight into electricity via solar panels, storing it in built-in batteries. As clean, quiet, and sustainable power solutions, they’ve become increasingly popular for both home emergency use and off-grid adventures.
Many modern solar generators can deliver up to 2,400W of continuous output and 3,600W surge power, making them capable of running essential appliances like refrigerators, power tools, and medical devices. They’re an eco-friendly emergency power option. Here are their key features:
Advantages:
Eco-Friendly: Powered by renewable energy, they produce no noise or emissions, making them suitable for indoor and outdoor use.
Low Operating Costs: No fuel is required, just sunlight, resulting in minimal long-term costs.
Portability: Many solar generators are lightweight and designed for easy transport, ideal for camping or travel.
Low Maintenance: They require minimal upkeep, typically just keeping the solar panels clean.
Disadvantages:
Weather-Dependent: Charging is less effective on cloudy days or at night, limiting power output.
Higher Initial Cost: Solar generators and panels can be expensive to purchase upfront.
Limited Power Output: Compared to propane generators, solar generators typically have lower wattage, unsuitable for high-power devices.
Propane Generator vs. Solar Generator: Which to Choose?
Feature
Propane Generator
Solar Generator
Energy Source
Propane fuel
Solar energy
Power Output
High, suitable for large devices
Lower, best for small devices
Operating Cost
Higher due to fuel and maintenance
Near-zero operating cost
Eco-Friendliness
Produces noise and emissions
No noise or emissions, eco-friendly
Portability
Heavier, less portable
Lightweight, highly portable
Use Cases
Long outages, high-power needs
Outdoor activities, short outages
Choosing the Right Option:
If you live in an area prone to extended outages or need to power high-wattage devices (like air conditioners or refrigerators), a propane generator is likely the more reliable choice.
If you prioritize eco-friendliness, portability, and low maintenance, or need power for outdoor activities or short-term emergencies, a solar generator is ideal.
Hybrid Approach: Some users opt for both propane and solar generators to cover different scenarios. For example, a solar generator for daily small devices and a propane generator as a backup for prolonged outages.
Ampace Solar Generators for Emergencies
Ampace is committed to providing reliable emergency power solutions for all households. Ampace solar generators combine portable power stations with Ampace solar panels, offering a clean and sustainable energy solution during emergencies. All Ampace power stations deliver pure sine wave output and stable voltage to ensure the safe operation of all your appliances. The high-capacity batteries help you get through every power outage with ease.
Ampace Andes 1500
Ampace Andes 1500 is a high-capacity portable power station with a massive 1,462 Wh battery and 13 output ports, ready to charge multiple devices at once. Paired with a portable solar panel, it allows you to achieve energy self-sufficiency.
In addition, the Ampace Andes 1500 supports external battery expansion. When you connect an expansion battery to the Andes 1500, the usable battery capacity reaches 2,924 Wh. One Andes 1500 can connect up to seven expansion batteries, offering a maximum expanded capacity of 11 kWh—perfect for home emergencies and long-term power outages.
Ampace Andes 600 Pro
The Ampace Andes 600 Pro is a good option for outdoor enthusiasts. Equipped with a 584Wh battery capacity and 9 versatile output ports, it’s capable of powering a wide range of devices.
The Andes 600 Pro features a LiFePO₄ (LFP) battery with a lifespan of 10 years. Even after more than 2,000 cycles, it can still retain 80% of its capacity. It supports powering devices such as CPAP machines, making it a reliable companion for both health-related needs and everyday backup power.
FAQ
What is a personal emergency evacuation plan?
A personal emergency evacuation plan (PEEP) is a customized safety strategy that outlines how an individual—especially someone with mobility or health challenges—can safely exit a building during an emergency like a fire or power outage. It includes escape routes, assistance roles, and communication procedures.
What size emergency generator do I need?
To determine the right emergency generator size, add up the wattage of essential appliances. For basic use (lights, phone, router), 500–1,000W is enough. If you need to power a fridge, microwave, or medical devices, aim for 1,500–3,000W. For whole-home backup during long outages, consider a generator over 5,000W.
How does an emergency action plan benefit your workplace?
An emergency action plan (EAP) enhances workplace safety by outlining clear procedures for evacuation, communication, and emergency response. It helps employees act quickly and confidently during fires, power failures, or natural disasters—reducing injuries, confusion, and business downtime.
What is the best emergency solar generator for home use?
The best emergency solar generator offers high battery capacity (1,000Wh or more), fast solar charging, pure sine wave output, and multiple ports. Models like the Ampace Andes 1500, with 1,462Wh capacity and expandability up to 11kWh, are ideal for powering fridges, medical equipment, and home electronics during outages.
 Ampace - 2025-07-10
Ampace - 2025-07-10

Power Backup
 Ampace - 2025-07-01
Ampace - 2025-07-01
How to Charge a Phone Without Electricity
Table of Contents
Understanding the Basics of Phone Charging
How to Charge Your Phone
How to Charge Your Phone Without a Charger
How Much Power Does a Phone Consume?
Ampace Portable Charging Stations for Phones
How to Maintain Your Phone’s Battery
Common Phone Charging FAQs
Final Thoughts
Properly charging your smartphone is essential for maintaining its performance and extending its battery life. With modern phones relying on lithium-ion batteries, understanding the basics of charging, alternative methods, power consumption, and battery care can make a significant difference. In this guide, we’ll cover everything you need to know about charging your phone, including how to charge without a charger, power usage, portable charging solutions like Ampace stations, battery maintenance tips, and answers to common charging questions.
Understanding the Basics of Phone Charging
Smartphone charging involves supplying power to a lithium-ion battery, which is lightweight, charges quickly, and offers long-lasting power compared to older battery technologies. Most phones use USB-C or Lightning cables (for iPhones) and support a range of charging speeds, from standard 5W to fast charging at 20W or higher.
Key Charging Parameters
Voltage: Most phone chargers output 5V for standard charging, while fast chargers may use 9V or 12V. Always ensure the charger’s voltage matches your phone’s requirements to avoid damage.
Amperage: Measured in amps (A), this determines how much current flows to your phone. Common values are 1A to 3A, with higher amperage enabling faster charging if supported.
Wattage: Calculated as voltage × amperage, wattage indicates the charger’s power output. For example, a 5V/2A charger delivers 10W.
To charge efficiently, use a charger and cable that match your phone’s specifications. For instance, iPhones support USB-C Power Delivery for faster charging, while Android devices often use protocols like Qualcomm Quick Charge.
Milliamps (mA) and amps (A) are units of current. Understanding their concepts and conversion methods can help you calculate and save energy, leading to significant savings in money and time, especially when choosing energy-efficient appliances.
SEE ALSO Milliamps to Amps (mA to A) Conversion Guide
How to Charge Your Phone
Follow these steps for safe and effective charging:
Use the Original Charger and Cable: Manufacturers design chargers to match their devices’ needs. For example, Apple recommends USB-C Power Delivery chargers for iPhone 15 models.
Plug into a Reliable Power Source: Connect your charger to a wall outlet or a high-quality power bank. Avoid low-quality chargers, as they may deliver inconsistent power.
Monitor Charging Time: Most phones charge to 80% quickly, then slow down to protect the battery. Avoid leaving your phone plugged in overnight unnecessarily.
Enable Optimized Charging (if available): Features like Apple’s Optimized Battery Charging learn your habits and delay charging past 80% to reduce battery wear.
For MagSafe-compatible iPhones (e.g., iPhone 12–16), you can use a MagSafe Charger for wireless charging, which aligns magnetically for efficient power delivery.
How to Charge Your Phone Without a Charger
If you don’t have a charger, try these alternatives:
USB Port on a Computer: Connect your phone to a laptop or desktop USB port. Ensure the port’s output (e.g., 5V/0.5A) is sufficient, though charging may be slower.
Power Bank: A portable power bank with adequate capacity (e.g., 10,000mAh) can charge your phone multiple times. Choose one with matching voltage and amperage.
Wireless Charging Pad: If your phone supports wireless charging (e.g., Qi standard), use a compatible pad. Note that wireless charging is slower than wired.
Car Charger: Use a car charger with a USB port or cigarette lighter adapter for on-the-go charging.
Solar Charger: In emergencies, a solar-powered charger can work, though it’s slower and depends on sunlight.
Always verify compatibility to avoid damaging your phone. For example, using a high-power laptop charger (e.g., 65W) without proper voltage regulation can harm your device.
How Much Power Does a Phone Consume?
Phone power consumption varies based on the device and charging speed:
Standard Charging: Typically 5–10W (5V/1–2A).
Fast Charging: Ranges from 15–30W for most smartphones, with some Android devices supporting up to 65W.
Idle Consumption: When not charging, phones use minimal power (0.1–0.5W) for background tasks.
For example, an iPhone 15 charging at 20W will consume 20 watts per hour during fast charging. To calculate energy use, multiply wattage by charging time. A full charge for a 3,000mAh battery at 20W might take about 1–2 hours, consuming roughly 0.02–0.04 kWh. Check your phone’s manual or manufacturer’s website for exact specs.
Ampace Portable Charging Stations for Phones
Ampace portable power stations are ideal for charging phones during travel, camping, or power outages. They offer high-capacity, durable solutions with three models:
Ampace Andes 300 (266Wh): Charges a smartphone ~20–24 times, 300W output, 45-min fast charge (0–80%), 6 ports (USB-C PD 100W, USB-A). Lightweight at 8.2 lbs, perfect for camping.
Ampace Andes 600 Pro (584Wh): Charges a smartphone ~45–50 times, 600W output (1800W surge), 1-hour fast charge (0–80%), 9 ports. Weighs 19.4 lbs, great for RV trips or home backup.
Ampace Andes 1500 (1462Wh): Charges a smartphone ~120–130 times, 2400W output (3600W surge), 55-min full charge, 13 ports. At 28.6 lbs, ideal for home outages or heavy appliances.
Key Features: Support fast charging (Power Delivery, Quick Charge), LiFePO4 batteries (2,000–6,000 cycles), solar charging, and app control. Choose the Andes 300 for portability, 600 Pro for balance, or 1500 for maximum power.
Ampace portable power stations use pure sine wave inverters, which ensure higher-quality AC output that closely matches the standard of the grid.
SEE ALSO What You Need to Know About Pure Sine Wave Inverters
How to Maintain Your Phone’s Battery
Proper battery care extends your phone’s lifespan and performance. Follow these tips:
Avoid Extreme Temperatures: Keep your phone between 32°F and 95°F (0°C–35°C) to prevent battery degradation.
Charge Between 20% and 80%: Lithium-ion batteries last longer when kept in this range, as full charge/discharge cycles increase wear.
Use Optimized Charging Features: Enable settings like iPhone’s Optimized Battery Charging to reduce chemical aging.
Avoid Overcharging: Unplug your phone once it’s fully charged, or use smart charging features to limit overcharging.
Update Software: Keep your phone’s OS updated for battery optimization improvements.
Avoid Cheap Chargers: Low-quality chargers can deliver unstable power, harming the battery.
Common Phone Charging FAQs
Can a high-wattage charger damage my phone?
Modern phones have built-in protections to regulate power intake. A high-wattage charger (e.g., 87W) won’t damage your phone if it’s compatible, but it won’t charge faster than the phone’s maximum supported wattage.
Should I fully charge and discharge my phone?
No. Modern lithium-ion batteries don’t require full charge/discharge cycles. Keeping the battery between 20% and 80% is better for longevity.
Is it safe to charge my phone overnight?
It’s generally safe due to built-in charging protections, but frequent overnight charging can accelerate battery aging. Use optimized charging features to minimize this.
Can I use a laptop charger to charge my phone?
Yes, if the voltage and connector match (e.g., 5V USB-C). However, laptop chargers with higher voltages (e.g., 20V) may not be compatible and could damage your phone.
Why is my phone charging slowly?
Slow charging can result from a low-power charger, a damaged cable, background apps consuming power, or high temperatures. Check your charger’s specs and close unnecessary apps.
Final Thoughts
Charging your phone correctly ensures optimal performance and battery longevity. Stick to manufacturer-recommended chargers, avoid extreme temperatures, and leverage features like optimized charging. For situations without a charger, options like power banks or Ampace portable charging stations offer reliable alternatives. By understanding your phone’s power needs and following best practices, you can keep your device running smoothly for years.
Read More
How to Power Your Drone with a Portable Station?
What You Need to Know About Pure Sine Wave Inverters?
Breaking Down the Costs of Life on the Road: Full-Time RV Living
The Two Best Portable Solar Panels 2025 Updated
Embrace Off-Grid Living with Solar-Powered Cabins
 Ampace - 2025-07-01
Ampace - 2025-07-01

Power Backup
 Ampace - 2025-06-26
Ampace - 2025-06-26
How many amps does a Switch 2 Use
Table of Contents
How Many Amps Does a Switch2 Use?
How Many Watts Does the Switch2 Controller Use?
How Long Can Ampace Run A Switch2?
Ampace Portable Power Stations for Nintendo Switch 2
With the hot release of Switch 2, this new generation of handheld brings gamers a freer off-grid gaming experience. If you're a hardcore gamer, you often have to carry a heavy console and monitor when you want to go out and play console games. Today, a high-performance portable device can easily meet the demand for both image quality and performance, making it possible to play anytime, anywhere.
When using Switch 2 outdoors for extended periods of time, a backup power supply is essential. Whether you're a hardcore gamer or a casual user, an efficient portable charging solution can not only keep your device running, but also handle unexpected situations such as power outages. Before we get to the solution, you may be concerned about the Switch 2's power consumption - this blog will delve deeper into this issue and examine how a portable power supply can provide reliable battery life.
The Ampace Portable Power Station is ideal for just such scenarios. With its high-capacity output, long-lasting battery life, and multiple ports, it can keep multiple devices, such as the Switch 2, powered up. Whether you're at the campsite, on the go, or enjoying some quiet time on the balcony, Ampace is the power to keep you going.
How Many Amps Does a Switch2 Use?
The Switch 2’s power usage varies depending on its operating state—whether you're actively gaming, browsing the HOME Menu, or leaving the console in sleep mode. In regions like the United States, the Switch 2 operates at 120 volts (V), which we’ll use as our reference. To calculate amps, we use the formula:
Amps = Watts ÷ Volts
Game Mode (TV Mode): According to official specifications, the Switch 2 draws approximately 19W while running a game in TV mode.
At 120V, this equals: 19W ÷ 120V = 0.16 amps
HOME Menu (Idle Mode): While navigating the HOME Menu, power consumption drops to around 8W.
8W ÷ 120V = 0.067 amps
Sleep Mode: In sleep mode, power consumption depends on network activity:
Wi-Fi connected, no LAN: 0.5W → 0.5W ÷ 120V = 0.0042 amps
Wired LAN connection maintained: 5W → 5W ÷ 120V = 0.042 amps
Even when turned off, the Switch 2 draws a small amount of standby power:
0.5W ÷ 120V = 0.0042 amps
Mode
Power (W)
Amps (at 120V)
Game Mode (TV Mode)
19 W
0.16 A
HOME Menu
8 W
0.067 A
Sleep Mode (Wi-Fi only)
0.5 W
0.0042 A
Sleep Mode (LAN maintained)
5 W
0.042 A
Power Off
0.5 W
0.0042 A
How Many Watts Does the Switch2 Controller Use?
The power consumption of Switch 2 controllers—whether official Joy-Cons, the Pro Controller, or most third-party options—is typically around 0.1 watts, which is extremely low and can be considered negligible. Below are their battery capacities and typical battery life. You can easily recharge them using a power bank or portable power station.
Joy-Con 2 Controller
Battery capacity: 500 mAh
Battery life: Up to ~20 hours
Estimated power draw: ~0.09 watts
Switch 2 Pro Controller
Battery capacity: 1070 mAh
Battery life: Around 40 hours
Estimated power draw: ~0.10 watts
Note: The original Switch Pro Controller (CTR-003 model) had a 1300 mAh battery. The Switch 2 Pro appears to use a slightly smaller 1070 mAh cell with similar battery life due to improved efficiency.
Third-Party Controllers
Battery capacity: Typically, 600–1200 mAh
Battery life: Around 10–30 hours
Estimated power draw: ~0.1–0.2 watts (varies by brand)
How Long Can Ampace Run A Switch2?
Ampace is one of the world’s leading battery solution providers. Our solar generators and portable power stations are designed to deliver reliable, continuous power—whether you're indoors or exploring the outdoors. Whether you need a backup power supply for your home or a solar-powered generator on the go, the Andes Series is your ideal choice.
The Nintendo Switch 2 features a 5,220 mAh battery (≈19.3 Wh at 3.7 V), offering around 2 to 6.5 hours of gameplay on a single charge. While you're away from home, Ampace Andes power stations can recharge your console multiple times—and even support extended play in TV mode when paired with a portable screen.
Estimated Full Charges per Model
Andes 300: 266Wh ÷ 19.3 ≈ 13.8 charges
Andes 600 Pro: 584Wh ÷ 19.3 ≈ 30.3 charges
Andes 1500: 1,462Wh ÷ 19.3 ≈ 75.7 charges
TV Mode with a Portable Screen
When using TV mode, Ampace power stations can simultaneously power both the Nintendo Switch 2 and a portable display. For such scenarios, you can use the Ampace power station to power the Nintendo Switch 2 and the screen at the same time.
Model
Capacity
Handheld Charges
TV Mode Hours
Andes 300
266 Wh
≈ 13.8 charges
≈ 10 hrs
Andes 600 Pro
584 Wh
≈ 30.3 charges
≈ 21.6 hrs
Andes 1500
1,462 Wh
≈ 75.7 charges
≈ 54 hrs
Ampace Portable Power Stations for Nintendo Switch 2
Ampace Andes 1500
Ampace Andes 1500 is a high-capacity portable power station with a massive 1,462 Wh battery and 13 output ports, ready to charge multiple devices at once. Paired with a portable solar panel, it’s the ideal solution for outdoor camping, RV living, emergency backup power, and more—delivering convenience and reliable energy wherever you go.
Ampace Andes 600 Pro
The Ampace Andes 600 Pro is a good option for outdoor enthusiasts. Equipped with a 584Wh battery capacity and 9 versatile output ports, it’s capable of powering a wide range of devices—from smartphones and laptops to mini fridges and gaming consoles like the Nintendo Switch2.
Whether you’re camping, traveling, or preparing for power outages, the Andes 600 Pro delivers stable, efficient, and safe energy wherever you go. Its compact design, fast charging support, and pure sine wave AC output make it a dependable companion for both indoor and off-grid scenarios.
Ampace Andes 300
For users who need portable power but prefer to travel light, the Ampace Andes 300 is the perfect solution. With a 266Wh capacity and weighing only 8.2 lbs, it features six versatile output ports, including USB-C PD port—ideal for powering newer gaming devices like the Nintendo Switch2. It’s also a great companion for remote work and mobile lifestyles, keeping your small devices charged and ready wherever you go.
FAQ
How to charge Nintendo Switch 2 controllers?
You can charge the Joy-Con 2 controllers by sliding them onto the console while it's charging. If you're using a Pro Controller or playing in TV mode, you can charge via a USB-C cable connected to the Switch dock, a wall adapter, or a portable power station like the Ampace Andes.
How to charge a Pro Controller for Nintendo Switch 2?
Plug it into any USB-C power source—like the Ampace Andes 300/600 Pro/1500—or directly into the Switch dock using the provided cable. Charging while playing is supported.
How long does it take to charge a Switch 2 controller?
Joy-Con 2: ~3.5 hours to full charge
Pro Controller: ~6 hours to full charge
You can charge both while using them if needed, especially with a reliable portable power station.
Do Switch 2 controllers use a lot of power?
Not at all. Joy-Con 2 controllers use about 0.09 watts, and the Pro Controller uses around 0.10 watts.
How do you charge the Nintendo Switch 2?
You can charge the Switch 2 using the official USB-C charger or via a portable power station like the Ampace Andes Series, which supports stable DC and AC output—ideal for on-the-go gaming or emergency backup.
Disclaimer:The operating times provided for devices powered by Ampace are estimates only. Actual performance may differ based on various factors. For precise results, please consult real-world usage data.
 Ampace - 2025-06-26
Ampace - 2025-06-26
Page 2 of 7












